Sorption behavior is determined by a partial pressure gradient, in which in accordance with the diffusion law water vapor always flows from the higher to the lower partial pressure until a vapor pressure equilibrium is established. Intake of water vapor is here known as adsorption, while release of water vapor is known as desorption (see Fig. 3).
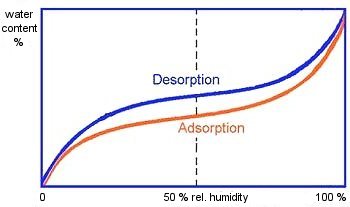 |
Figure 3: Adsorption and desorption curve; Tietke [58] Y-axis: water content X-axis: relative humidity |